In today’s competitive landscape, organizations must continuously assess their performance to ensure they are on the right path toward achieving their goals. When resources, capital, and technology are not utilized effectively, companies may struggle to reach their full potential. This is where gap analysis becomes a crucial tool for improvement. Gap analysis is a crucial tool for organizations seeking to identify discrepancies between their current performance and desired goals. While many organizations utilize the BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) modeling approach for gap analysis, several other powerful business analysis methods can effectively complement this process.
What is Gap Analysis?
A gap analysis, often referred to as a needs analysis, helps organizations identify the disparity between their current state and desired future state. By conducting a gap analysis, companies can evaluate their goals, assess their performance, and determine whether they are on track to achieve their objectives.
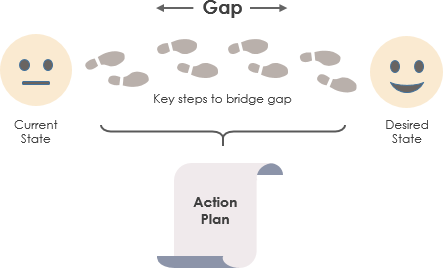
Originating in the 1980s, gap analysis is a method for assessing exposure to various term structure movements. While it is considered more complex than duration analysis, its application in organizational performance assessment is invaluable.
The Importance of Gap Analysis
- Identifies Performance Gaps: Helps organizations pinpoint where they are falling short of their goals.
- Guides Strategic Planning: Offers insights that inform future strategies and initiatives.
- Enhances Resource Allocation: Aids in reallocating resources to areas where they can have the most impact.
- Improves Decision-Making: Provides a clearer understanding of internal and external factors affecting performance.
Gap Analysis Tools
While BPMN modeling is a popular and effective approach for conducting gap analysis, leveraging other business analysis methods can enhance the overall process. By integrating tools like SWOT, TOWS, Fishbone Diagrams, the McKinsey 7S Framework, and PEST analysis, organizations can gain deeper insights into their performance gaps and develop more comprehensive strategies for improvement. This multifaceted approach not only clarifies where gaps exist but also empowers organizations to take informed action toward achieving their goals.
To facilitate effective gap analysis, various tools are available, each tailored to specific aspects of the process. Here are some of the best business analysis tools for conducting a gap analysis:
1. SWOT Analysis
Overview: SWOT analysis evaluates a company’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.

- Use in Gap Analysis:
- Internal Factors: Assess internal strengths and weaknesses to determine areas for improvement.
- External Factors: Identify external opportunities and threats that may impact the organization’s ability to close performance gaps.
By understanding both internal and external factors, companies can strategically allocate resources and address weaknesses that hinder progress.
2.TOWS Analysis
Overview: TOWS analysis is an extension of the SWOT framework that focuses on developing strategic options based on the relationships between internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats.

- Use in Gap Analysis:
- Strategic Development: TOWS encourages organizations to create actionable strategies by matching internal capabilities with external conditions. For example, a company may leverage its strengths to capitalize on emerging opportunities or address weaknesses to mitigate potential threats.
- Action-Oriented Approach: By exploring how strengths can overcome threats or how weaknesses can be improved to seize opportunities, TOWS analysis provides a practical roadmap for strategic planning and resource allocation.
Incorporating TOWS analysis into the gap analysis process enhances strategic decision-making by ensuring that organizations not only understand their current position but also develop targeted strategies to bridge the gaps effectively.
3. Fishbone Diagram
Overview: Also known as a cause-and-effect or Ishikawa diagram, this tool helps identify the root causes of problems.
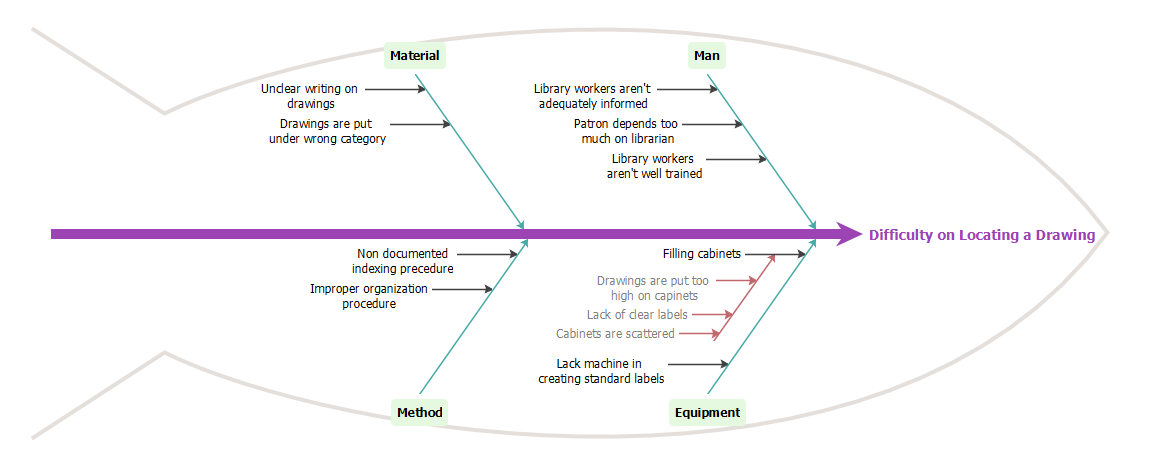
- Use in Gap Analysis:
- Problem Identification: Place the main problem at the center and branch out to explore potential causes.
- Creative Problem-Solving: Break down complex issues into manageable components, facilitating targeted solutions.
This visual approach encourages collaborative thinking and can reveal underlying issues that contribute to performance gaps.
4. McKinsey 7S Framework
Overview: This McKinsey 7S Framework model focuses on seven elements—Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Skills, Style, and Staff—that affect organizational performance.
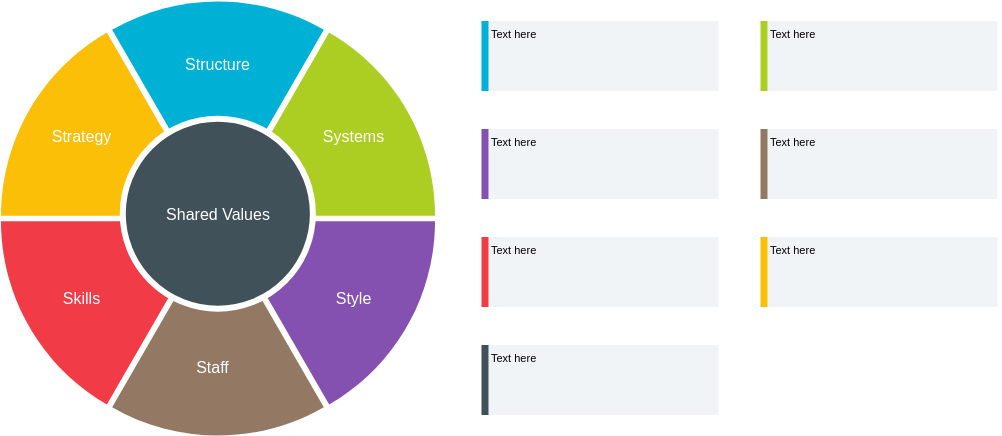
- Use in Gap Analysis:
- Holistic Assessment: Evaluate how each element aligns with organizational goals and identify areas needing improvement.
- Iterative Monitoring: Regularly review and adjust strategies based on performance assessments.
By examining these interconnected elements, organizations can align their operations with long-term objectives.
5. PEST Analysis
Overview: PEST analysis examines external factors—Political, Economic, Social, and Technological—that can impact an organization.
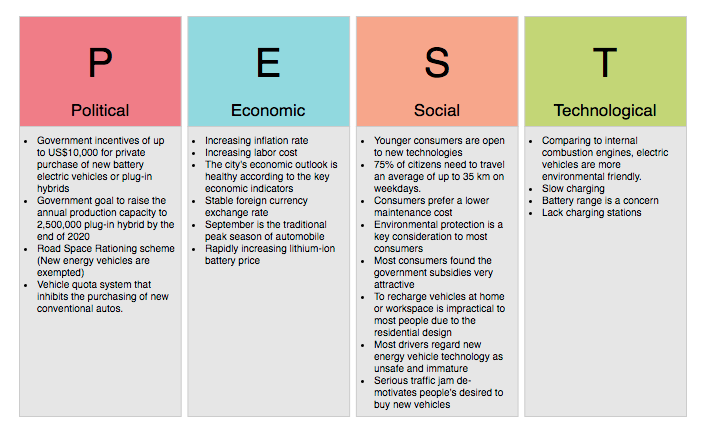
- Use in Gap Analysis:
- External Insights: Identify external factors that may create or exacerbate performance gaps.
- Strategic Adaptation: Understand how changes in the external environment can influence organizational strategy.
Incorporating external factors into the gap analysis process enables organizations to better anticipate and respond to challenges.
Summary Table of Gap Analysis Methods with Examples
| Analysis Tool | Overview | Relevance to Gap Analysis | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| SWOT Analysis | Evaluates Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats. | Identifies internal and external factors affecting performance; guides resource allocation and strategy. | A tech company identifies strong R&D (Strength) but faces tough competition (Threat) in the market. |
| TOWS Analysis | Matches internal strengths and weaknesses with external opportunities and threats. | Develops actionable strategies to leverage strengths and address weaknesses; provides a practical roadmap. | A startup leverages its innovative product (Strength) to enter a growing market (Opportunity) while addressing its limited funding (Weakness). |
| Fishbone Diagram | Visual tool for identifying root causes of problems. | Breaks down complex issues into manageable components; encourages collaborative problem-solving. | A retail store uses a fishbone diagram to identify causes of high customer complaints, such as long wait times and stock shortages. |
| McKinsey 7S | Focuses on seven elements: Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Skills, Style, Staff. | Assesses alignment of key elements with organizational goals; identifies areas needing improvement. | A nonprofit organization reviews its structure and skills (soft elements) to align with its mission and improve service delivery. |
| PEST Analysis | Analyzes external factors: Political, Economic, Social, Technological. | Identifies external factors affecting performance gaps; aids in strategic adaptation to environmental changes. | A pharmaceutical company assesses potential regulations (Political) that could impact drug pricing and market access. |
This revised table summarizes the relevant analysis methods for conducting a gap analysis, with TOWS analysis included and providing clear examples for each method’s application.
Conclusion
Gap analysis is a vital tool for organizations seeking to optimize their performance and achieve their goals. By utilizing effective business analysis tools such as SWOT, Fishbone Diagrams, McKinsey 7S, Nadler-Tushman, and PEST analysis, companies can gain valuable insights into their current state, identify areas for improvement, and develop actionable strategies for closing performance gaps.
In a rapidly evolving business environment, embracing gap analysis and its associated tools will empower organizations to navigate challenges, leverage opportunities, and ultimately thrive in their respective markets.
Unlock Your Business Potential with Visual Paradigm Online!
Are you looking to enhance your gap analysis, streamline processes, and drive organizational success? Look no further than Visual Paradigm Online, one of the best software solutions available today!
Why Choose Visual Paradigm Online?
🔍 Comprehensive Toolkit: Visual Paradigm Online offers a robust set of tools for various analysis methods, including SWOT, TOWS, Fishbone Diagrams, McKinsey 7S, and PEST analysis. Whether you’re identifying strengths, weaknesses, or external factors, you have everything you need at your fingertips.
🎨 User-Friendly Interface: With an intuitive drag-and-drop interface, creating diagrams and models is a breeze. You can visualize complex ideas and processes quickly, making collaboration seamless across teams.
📊 Real-Time Collaboration: Work together with your team in real-time. Share insights, gather feedback, and make decisions faster than ever, regardless of your team’s location.
📈 Customizable Templates: Choose from a wide variety of templates tailored to each analysis method. Save time and ensure consistency across your projects with professionally designed layouts.
💻 Cloud-Based Access: Access your projects anytime, anywhere. With cloud storage, you can work on your analyses from any device, ensuring you never miss a beat.
🚀 Drive Strategic Decisions: With powerful visualization tools, you can easily communicate findings and recommendations to stakeholders, empowering informed decision-making.
Start Your Journey Today!
Transform the way you analyze and improve your business processes. Sign up for Visual Paradigm Online and experience the difference it can make in your gap analysis and overall strategic planning.
Don’t settle for less; empower your organization with the best tools for success! 🌟