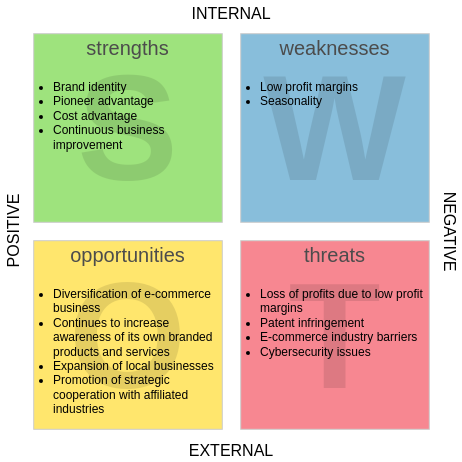
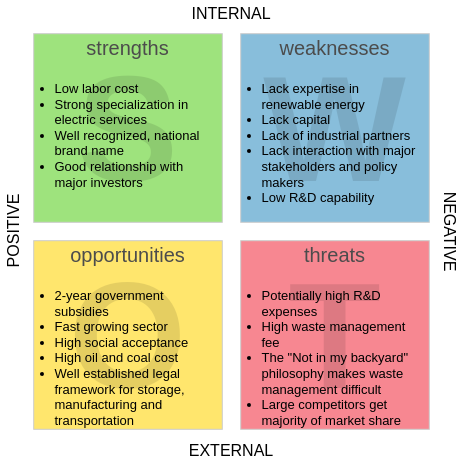
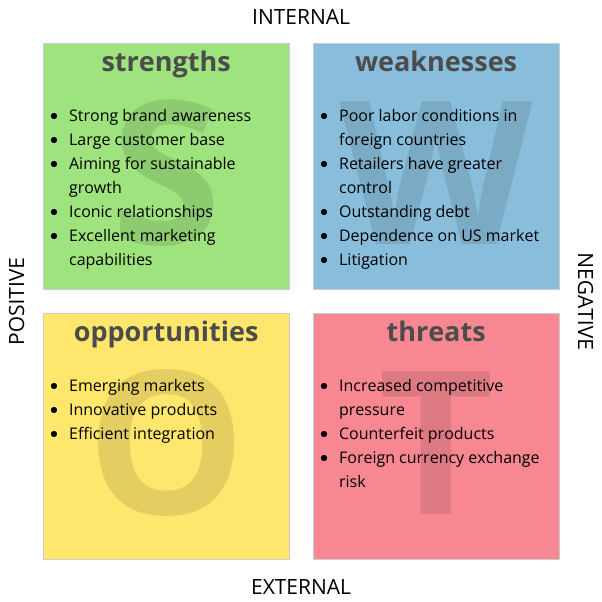
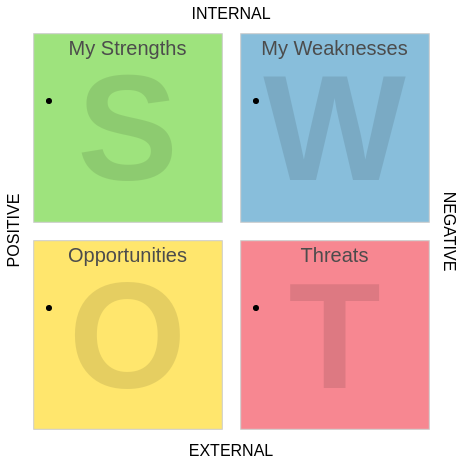
Mind mapping is an effective brainstorming tool that can help you identify the essential factors for a SWOT analysis. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use mind maps for this purpose and how to visualize your findings in a SWOT analysis chart.
Problem Description
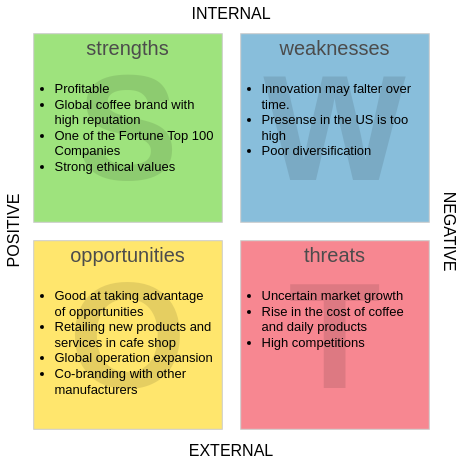
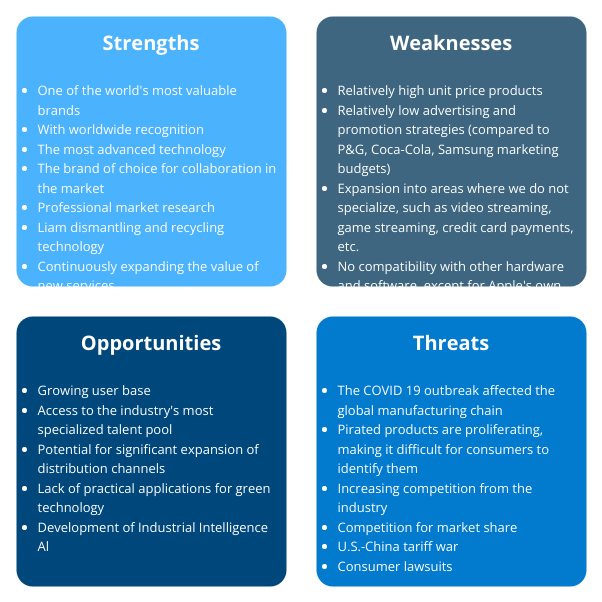
The image displays a mind map structured around the central theme of “SWOT Analysis.” It features four primary branches labeled Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. Each branch is further divided into sub-ideas that highlight specific factors relevant to the SWOT analysis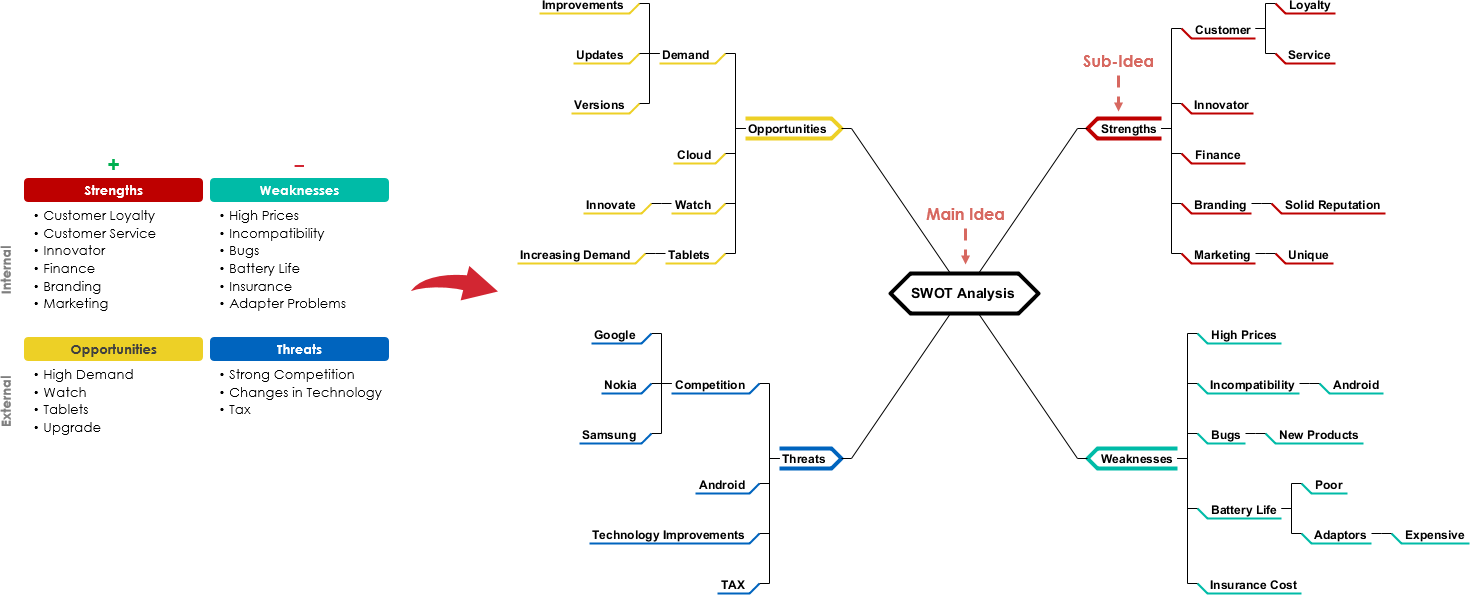
- Strengths include aspects like customer loyalty, innovative products, and a strong brand reputation.
- Weaknesses outline challenges such as high prices and issues with product availability.
- Opportunities point to external factors like emerging markets and technological advancements.
- Threats encompass competitive pressures and changes in technology.
Discovering Items for Each SWOT Category Using the Mind Map
1. Strengths
- Brainstorming Questions:
- What unique resources or capabilities does the organization possess?
- What do customers perceive as the organization’s strengths?
- Methods:
- Gather feedback from team members through discussions or surveys.
- Analyze past successes or achievements that contributed to the organization’s reputation.
2. Weaknesses
- Brainstorming Questions:
- What areas need improvement within the organization?
- What do customers or competitors identify as shortcomings?
- Methods:
- Conduct internal reviews or audits to identify operational inefficiencies.
- Encourage honest discussions within teams to surface concerns and challenges.
3. Opportunities
- Brainstorming Questions:
- What trends in the market could the organization capitalize on?
- Are there gaps in the market that the organization could fill?
- Methods:
- Research industry reports and market analyses to identify emerging opportunities.
- Engage in competitor analysis to spot areas where competitors are not fully meeting customer needs.
4. Threats
- Brainstorming Questions:
- What external factors could negatively impact the organization?
- How is the competitive landscape evolving?
- Methods:
- Stay updated on industry news and regulatory changes that could affect operations.
- Conduct SWOT analyses of competitors to understand their strengths and how they might pose threats.
The layout visually organizes the components of the SWOT analysis, allowing for easier understanding and analysis.
Step 1: Define Your Main Idea
- Start with the Central Topic:
- Write “SWOT Analysis” in the center of your mind map. This will be your main idea around which all other thoughts will revolve.
Step 2: Create Main Branches for Each SWOT Element
- Draw Four Main Branches:
- From the central topic, draw four branches labeled Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. Each branch represents a key component of the SWOT analysis.
Step 3: Brainstorm Ideas for Each Category
- Identify Strengths:
- Under the Strengths branch, brainstorm and list factors that give your organization a competitive advantage (e.g., strong brand reputation, loyal customer base, innovative products).
- Identify Weaknesses:
- Under the Weaknesses branch, list internal factors that may hinder your organization’s performance (e.g., high prices, limited market presence, lack of R&D).
- Identify Opportunities:
- Under the Opportunities branch, think about external factors that could benefit your organization (e.g., emerging markets, technological advancements, changing consumer preferences).
- Identify Threats:
- Under the Threats branch, list external challenges that could impact your organization negatively (e.g., increased competition, regulatory changes, economic downturns).
Step 4: Expand Your Ideas
- Add Sub-Branches:
- For each main branch, create sub-branches to delve deeper into specific points. For example:
- Under Strengths, you might add sub-branches for Customer Loyalty, Branding, and Innovative Products.
- Under Threats, you could include sub-branches for Competition and Technological Changes.
- For each main branch, create sub-branches to delve deeper into specific points. For example:
Step 5: Organize and Prioritize
- Review and Prioritize:
- Go through each branch and sub-branch. Determine which factors are the most critical or impactful. This will help you prioritize your findings for the SWOT analysis chart.
Step 6: Create a SWOT Analysis Chart
- Visualize Your Findings:
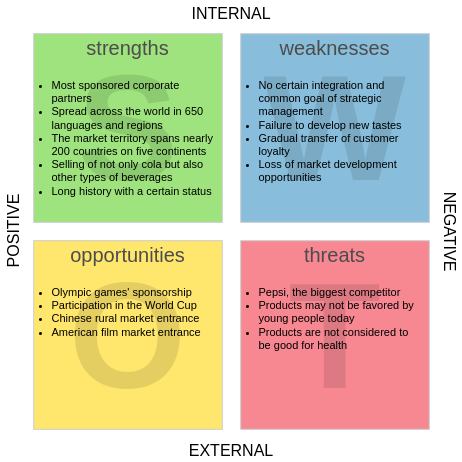
- Using the identified factors, create a SWOT analysis chart. Organize it in a 2×2 grid format:
- Top Left: Strengths
- Top Right: Weaknesses
- Bottom Left: Opportunities
- Bottom Right: Threats
- Using the identified factors, create a SWOT analysis chart. Organize it in a 2×2 grid format:
- Fill in the Chart:
- Transfer the prioritized factors from your mind map into the corresponding sections of the SWOT chart.
Step 7: Analyze and Plan
- Analyze the Chart:
- Review the completed SWOT analysis chart. Look for connections between the four categories, such as how strengths can be leveraged to take advantage of opportunities or mitigate threats.
- Develop Action Plans:
- Based on your analysis, create action plans that capitalize on strengths and opportunities while addressing weaknesses and threats.
Overall Process
- Collaborative Brainstorming: Engage team members in a brainstorming session where everyone can contribute ideas related to each category.
- Visual Representation: Use the mind map to visually organize and categorize thoughts. This helps to ensure that no important factors are overlooked.
- Continuous Refinement: Regularly revisit and update the mind map as new information or insights are gained, ensuring a dynamic and current SWOT analysis.
Conclusion
Using a mind map as a brainstorming tool for SWOT analysis helps in visually organizing thoughts and facilitating a comprehensive understanding of your organization’s strategic position. By following these steps, you can effectively identify essential factors and create a clear SWOT analysis chart to guide your decision-making process.
By following this structured approach, teams can effectively discover and categorize essential items for each component of the SWOT analysis, leading to a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s strategic position.