Strategic analysis is essential for understanding the external environment in which an organization operates. Here’s a structured guide to conducting a PESTLE and Porter’s Five Forces analysis.
What is PESTLE?
PESTLE (or PESTEL) is a strategic framework used to analyze the macro-environmental factors that might impact an organization. It encompasses six categories:
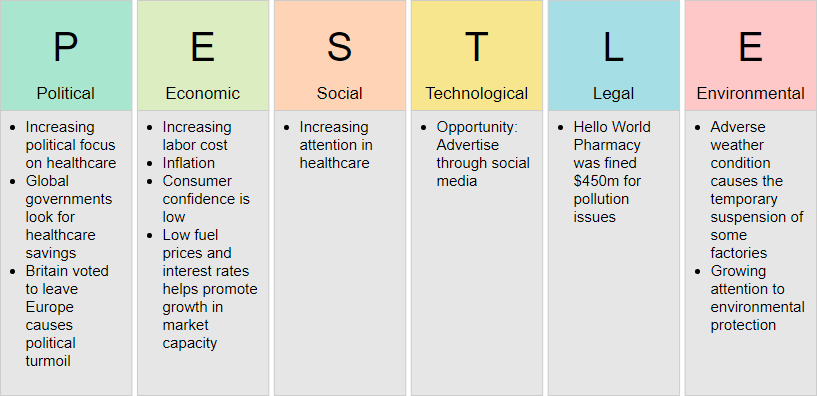
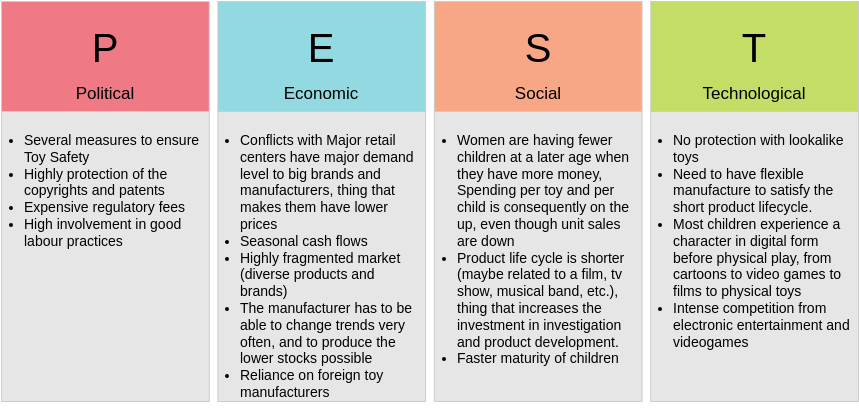
- Political: Government policies, regulations, and political stability that can affect business operations.
- Economic: Economic trends such as inflation, exchange rates, and economic growth that influence market conditions.
- Social: Societal trends, demographics, and cultural factors that affect consumer behavior.
- Technological: Technological advancements, R&D activities, and innovations that can impact operational efficiency.
- Legal: Laws and regulations, including employment law, consumer protection, and antitrust laws.
- Environmental: Ecological factors such as climate change, sustainability practices, and environmental regulations.
What is Porter’s Five Forces?
Porter’s Five Forces is a framework for analyzing the competitive dynamics within an industry. It includes five key forces:
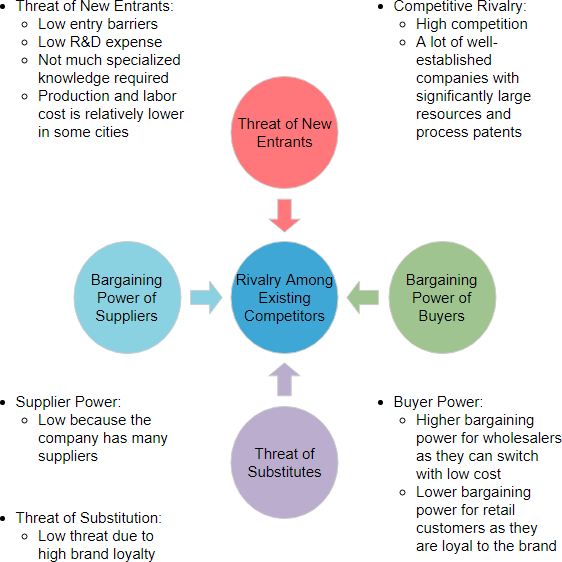
- Threat of New Entrants: The likelihood of new competitors entering the market, which can impact market share and profitability.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers: The power suppliers have to affect the cost and availability of inputs, impacting profitability.
- Bargaining Power of Customers: The influence customers have over pricing and quality, which can affect a company’s margins.
- Threat of Substitute Products: The risk that alternative products or services may replace existing offerings, impacting demand.
- Competitive Rivalry: The intensity of competition among existing players in the market, affecting pricing and profitability.
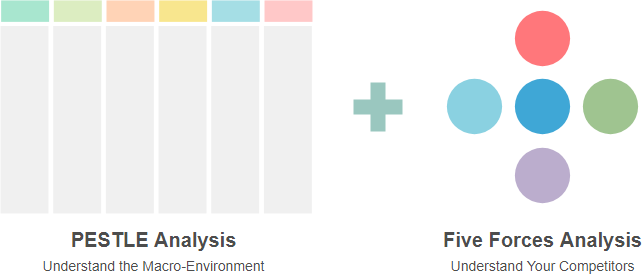
Combining PESTLE and Porter’s Five Forces analyses
Combining PESTLE and Porter’s Five Forces analyses offers several advantages for strategic planning and decision-making. Here are the key benefits:
1. Comprehensive Understanding of the Environment
- Holistic View: PESTLE provides insights into macro-environmental factors, while Porter’s Five Forces focuses on industry-specific dynamics. Together, they create a comprehensive understanding of both external influences and competitive pressures.
2. Identification of Opportunities and Threats
- Strategic Insights: By analyzing political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors alongside competitive forces, organizations can better identify potential opportunities for growth and threats that may impact their operations.
3. Enhanced Strategic Decision-Making
- Informed Choices: The integration of both analyses equips senior management with the necessary information to make informed strategic decisions, aligning organizational goals with market realities.
4. Improved Risk Management
- Proactive Approach: Understanding both the macro-environment and competitive landscape allows organizations to anticipate risks and develop strategies to mitigate them effectively.
5. Better Resource Allocation
- Efficient Planning: Insights from both analyses help organizations prioritize resources by identifying which areas require more focus and investment based on external and competitive pressures.
6. Increased Adaptability
- Responsive Strategies: Regularly updating both analyses allows organizations to remain agile, adapting strategies as external factors and competitive dynamics evolve over time.
7. Enhanced Competitive Advantage
- Strategic Positioning: By understanding both the external environment and competitive forces, organizations can better position themselves in the market, leveraging their strengths to capitalize on opportunities while addressing threats.
8. Facilitation of Long-Term Planning
- Sustainable Growth: The combination of insights from PESTLE and Porter’s analyses supports long-term strategic planning, ensuring that organizations are prepared for future changes in the business environment.
In summary, using PESTLE and Porter’s Five Forces together provides a robust framework for strategic analysis, leading to more effective planning, risk management, and competitive positioning.
PESTLE Combine Porter’s Five Forces Example
Let’s consider an example of a new electric vehicle (EV) manufacturer to illustrate how PESTLE and Porter’s Five Forces can be combined for strategic analysis.
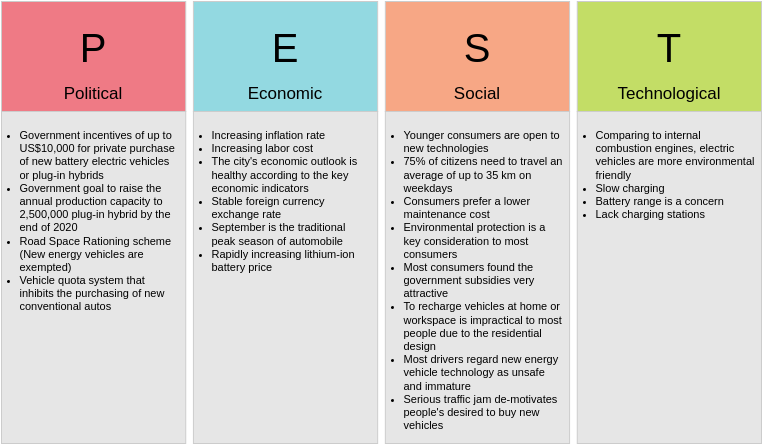
PESTLE Analysis for an Electric Vehicle Manufacturer
- Political:
- Government incentives for electric vehicles (e.g., tax credits, subsidies).
- Environmental regulations promoting clean energy and emissions reductions.
- Economic:
- Economic growth leading to increased consumer spending on automobiles.
- Fluctuating raw material costs (e.g., lithium for batteries) affecting production costs.
- Social:
- Growing consumer awareness and preference for sustainable and eco-friendly transportation.
- Urbanization leading to increased demand for electric vehicles in cities.
- Technological:
- Rapid advancements in battery technology improving range and charging speed.
- Innovations in autonomous driving technology that could enhance product offerings.
- Legal:
- Compliance with safety standards and regulations specific to electric vehicles.
- Intellectual property laws related to battery technology and automotive innovations.
- Environmental:
- Increasing concerns about climate change driving demand for electric vehicles.
- Regulations on waste management for batteries and vehicle end-of-life recycling.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis for the Electric Vehicle Industry
- Threat of New Entrants:
- Moderate threat due to high capital investment for manufacturing and technology development, but increasing interest in the EV market may attract new players.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers:
- High, as the supply of key components (like batteries) is concentrated among a few manufacturers, giving them leverage over pricing.
- Bargaining Power of Customers:
- Increasing power as consumers have multiple options, including traditional vehicles and other EV brands, leading to price sensitivity and demand for better features.
- Threat of Substitute Products:
- Moderate, with alternatives such as hybrid vehicles and public transportation available, but the unique benefits of EVs (like lower operating costs) can mitigate this threat.
- Competitive Rivalry:
- High, as established automotive brands and new startups are competing aggressively in the growing EV market, driving innovation and price competition.
Combining Insights for Strategy Development
- Opportunity Recognition:
- The PESTLE analysis highlights government incentives and consumer demand for sustainable products, suggesting that the company should focus on marketing its EVs as eco-friendly and financially advantageous due to subsidies.
- Risk Management:
- The high bargaining power of suppliers (Porter’s) indicates a risk in maintaining profit margins. The company could invest in developing partnerships or even vertical integration to secure supply chains for critical components.
- Strategic Positioning:
- Understanding the competitive rivalry (Porter’s) and social trends (PESTLE) supports a strategy of differentiation through advanced technology (e.g., longer battery life, faster charging) to attract tech-savvy consumers.
- Resource Allocation:
- The insights suggest prioritizing R&D investments in battery technology and marketing efforts to communicate sustainability benefits effectively, aligning with both external opportunities and competitive pressures.
Here’s a table summarizing the PESTLE and Porter’s Five Forces analyses for the electric vehicle manufacturer:
| Analysis Type | Factor | Details |
|---|---|---|
| PESTLE Analysis | Political | Government incentives for EVs (tax credits, subsidies); environmental regulations. |
| Economic | Economic growth increasing consumer spending; fluctuating raw material costs (e.g., lithium). | |
| Social | Growing consumer preference for sustainable transport; urbanization driving EV demand. | |
| Technological | Advancements in battery technology; innovations in autonomous driving. | |
| Legal | Compliance with safety standards; intellectual property laws for automotive tech. | |
| Environmental | Climate change concerns driving EV demand; regulations on battery recycling. | |
| Porter’s Five Forces | Threat of New Entrants | Moderate threat due to high capital investment; increasing interest may attract new players. |
| Bargaining Power of Suppliers | High power due to few suppliers of key components (batteries). | |
| Bargaining Power of Customers | Increasing power as consumers have many options; price sensitivity and demand for features. | |
| Threat of Substitute Products | Moderate threat from hybrids and public transport; unique benefits of EVs mitigate it. | |
| Competitive Rivalry | High competition from established brands and startups; drives innovation and price competition. |
This table provides a clear overview of the factors influencing the electric vehicle manufacturer’s strategic environment, integrating insights from both PESTLE and Porter’s Five Forces analyses.
Conclusion
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, conducting thorough strategic analyses is crucial for organizations aiming to thrive. The combination of PESTLE and Porter’s Five Forces frameworks provides a comprehensive approach to understanding both the macro-environment and the competitive dynamics within an industry.
By leveraging PESTLE analysis, companies can identify external factors—political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental—that may influence their operations and strategic direction. Meanwhile, Porter’s Five Forces analysis offers insights into the competitive pressures that shape market dynamics, including the threat of new entrants, supplier and customer bargaining power, the threat of substitutes, and competitive rivalry.
Together, these analyses empower organizations to make informed decisions, recognize opportunities, and mitigate risks effectively. This holistic view enables better resource allocation, enhances adaptability, and ultimately positions companies for sustainable success in an increasingly complex environment. Regularly updating these analyses ensures that organizations remain responsive to changes, fostering long-term growth and competitiveness.
By using both PESTLE and Porter’s Five Forces in the example above, the electric vehicle manufacturer can craft a well-informed strategy that leverages external opportunities while addressing internal and competitive challenges. This comprehensive approach enhances the likelihood of success in a rapidly evolving industry.