Value Chain Analysis (VCA) is a powerful tool for businesses seeking to enhance their competitive advantage and improve operational efficiency. By dissecting the components of a company’s activities, VCA helps organizations identify areas for optimization.
What is Value Chain Analysis?
Value Chain Analysis is a strategic framework developed by Michael Porter in his book, “Competitive Advantage,” published in 1985. It involves breaking down a company’s operations into primary and support activities to understand how each contributes to the overall value delivered to customers.
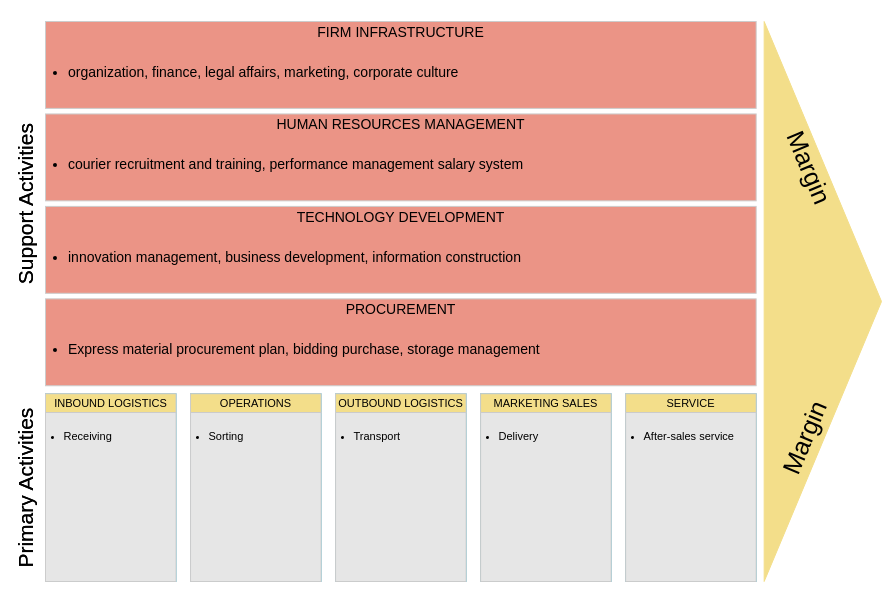
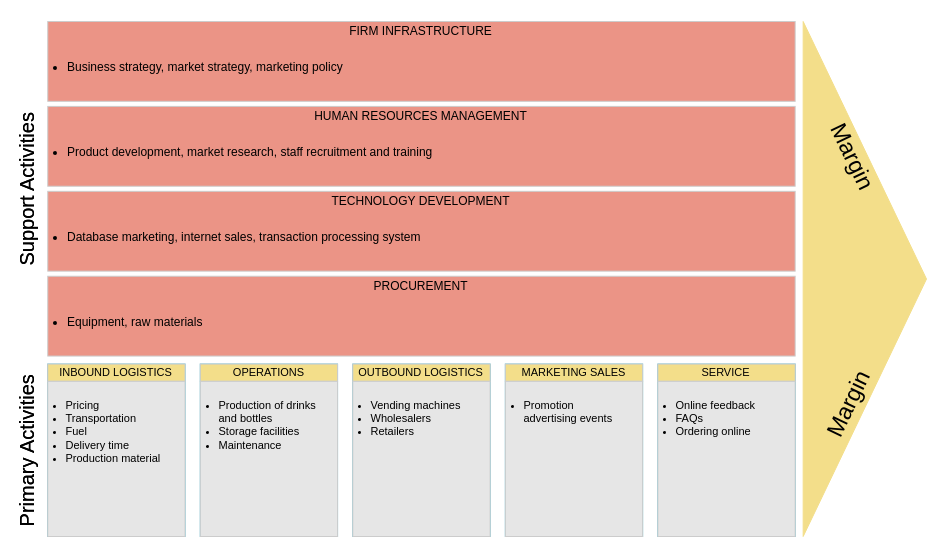
Primary Activities
- Inbound Logistics: Receiving, warehousing, and inventory management of raw materials.
- Operations: Processes that transform inputs into finished products or services.
- Outbound Logistics: Activities required to get the finished product to customers.
- Marketing and Sales: Activities aimed at creating buyer interest and facilitating sales.
- Service: Activities that maintain and enhance product value, including customer support.
Support Activities
- Firm Infrastructure: Organizational structure, management, planning, and finance.
- Human Resource Management: Recruitment, training, and employee development.
- Technology Development: Research and development, process automation, and other technology-related activities.
- Procurement: Acquiring goods and services necessary for operations.
Why Conduct a Value Chain Analysis?
Conducting a Value Chain Analysis offers several benefits:
- Identify Competitive Advantage: Understanding how each activity adds value helps businesses pinpoint their unique strengths.
- Cost Reduction: Analyzing costs associated with each activity can reveal inefficiencies and opportunities for cost savings.
- Enhance Customer Value: By improving activities that directly impact customer satisfaction, companies can strengthen their market position.
- Strategic Decision-Making: VCA provides insights that inform strategic decisions, such as mergers, acquisitions, and product development.
- Focus on Core Competencies: It helps organizations concentrate on what they do best and identify areas for outsourcing or collaboration.
How to Conduct a Value Chain Analysis
- Identify Activities: Begin by mapping out all primary and support activities within the organization.
- Analyze Each Activity: Evaluate how each activity adds value or incurs costs. Consider both qualitative and quantitative factors.
- Assess Linkages: Understand how activities interact and influence one another. Look for synergies that can enhance efficiency.
- Benchmark Against Competitors: Compare your value chain to those of competitors to identify best practices and areas for improvement.
- Develop an Action Plan: Based on the insights gained, create a strategy to optimize activities, reduce costs, and enhance customer value.
Who Should Conduct Value Chain Analysis?
Value Chain Analysis can be beneficial across various levels within an organization:
- Executives: For strategic planning and identifying areas for investment.
- Managers: To improve operational efficiency and team performance.
- Marketing Teams: To enhance customer engagement and value propositions.
- Financial Analysts: To assess cost structures and profitability.
External stakeholders, such as consultants and industry analysts, may also conduct VCA to provide insights to businesses.
When to Conduct Value Chain Analysis
- Strategic Planning: During the formulation of long-term strategies to understand competitive positioning.
- Operational Improvement Initiatives: When seeking to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
- Market Entry or Expansion: Before entering new markets or launching new products to evaluate the operational requirements.
- Post-Merger Integration: Following mergers or acquisitions to align operations and realize synergies.
- Regular Reviews: Continuous improvement efforts benefit from periodic VCA to remain competitive in changing markets.
Value Chain Analysis Examples
Here are enhanced examples of Value Chain Analysis, incorporating both primary and support activities for various companies across different industries.
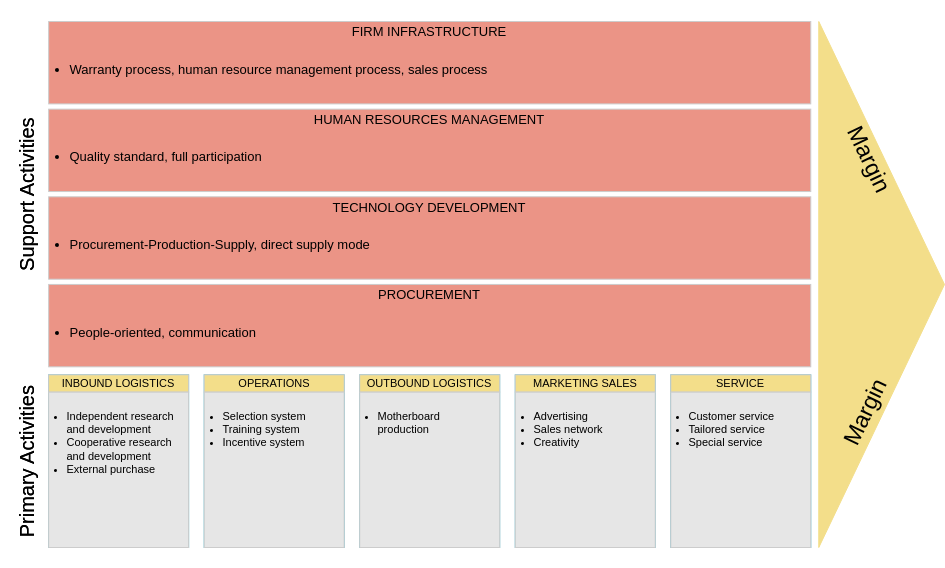
1. Manufacturing: Automobile Industry
Company: Ford Motor Company
- Primary Activities:
- Inbound Logistics: Efficient management of supplier relationships for parts like engines and tires.
- Operations: Streamlined assembly line processes to reduce production time and costs.
- Outbound Logistics: Effective distribution networks ensuring timely delivery to dealerships.
- Marketing and Sales: Strong branding campaigns emphasizing quality and innovation.
- Service: Comprehensive warranty and maintenance services that enhance customer loyalty.
- Support Activities:
- Firm Infrastructure: Robust management systems for coordinating production and supply chain logistics.
- Human Resource Management: Training programs focused on safety and efficiency for workers.
- Technology Development: Investment in automation and AI to improve manufacturing processes.
- Procurement: Strategic sourcing practices to negotiate better prices with suppliers.
Outcome: Ford enhances its competitive edge by optimizing both primary and support activities, leading to reduced costs and high-quality production.
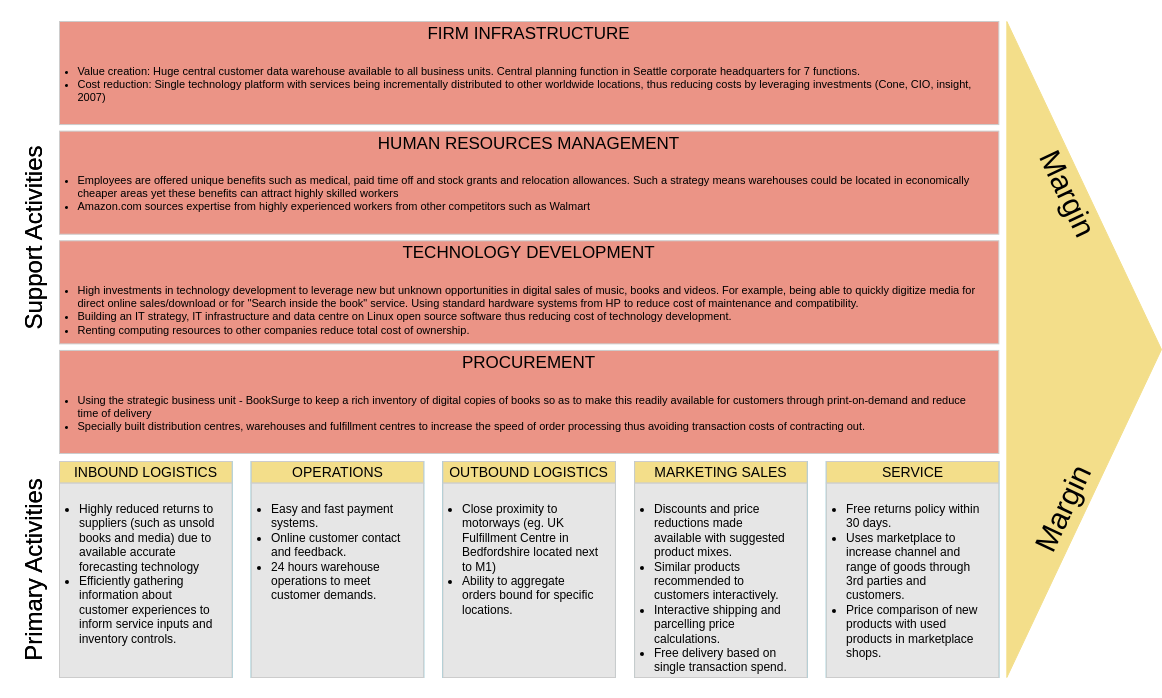
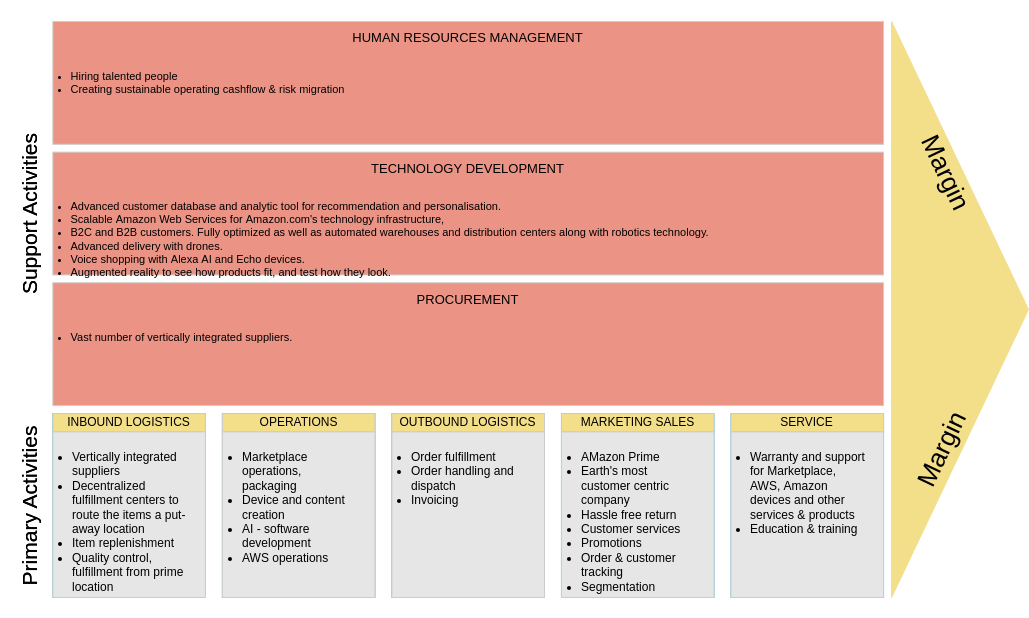
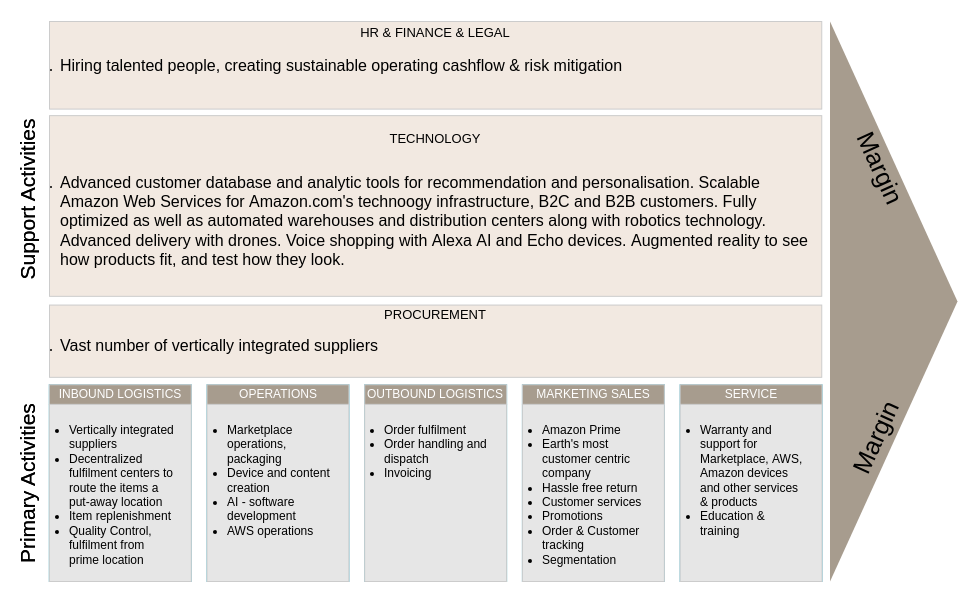
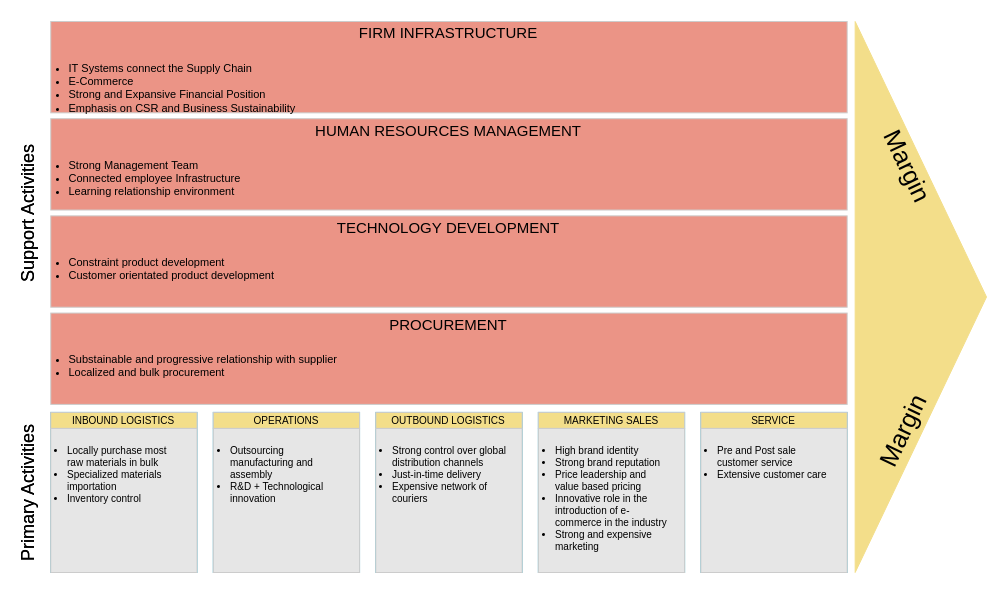
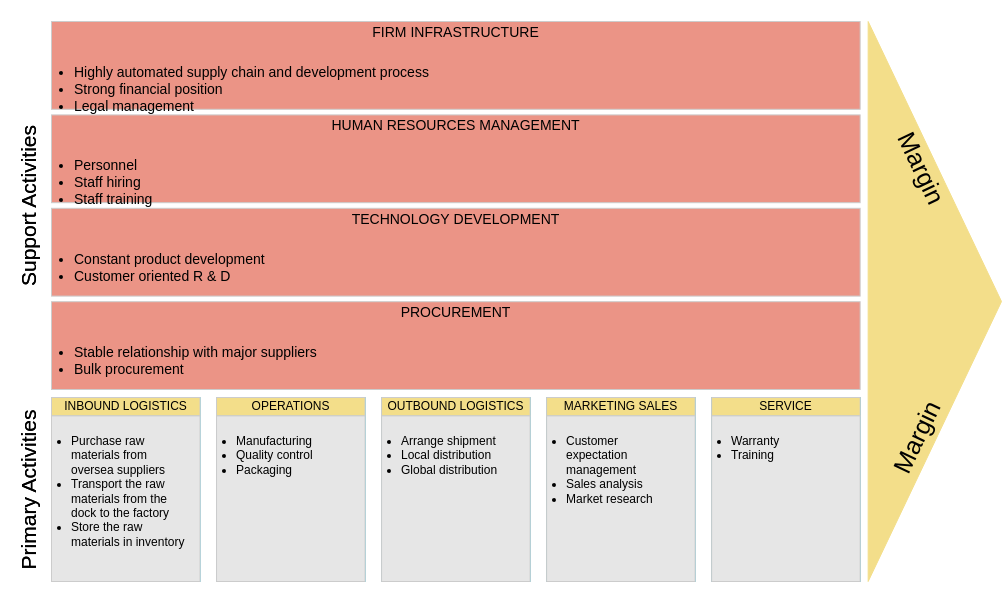
2. Retail: E-commerce
Company: Amazon
- Primary Activities:
- Inbound Logistics: Advanced supply chain management with multiple suppliers to ensure product availability.
- Operations: Sophisticated algorithms for seamless order processing and fulfillment.
- Outbound Logistics: Robust delivery network, including Prime shipping for quick access.
- Marketing and Sales: Personalized recommendations and targeted ads based on user behavior.
- Service: Efficient customer service and hassle-free return processes.
- Support Activities:
- Firm Infrastructure: Strong IT infrastructure supporting massive data processing and website functionality.
- Human Resource Management: Continuous training and development programs for staff.
- Technology Development: Investment in cloud computing and machine learning to enhance user experience.
- Procurement: Bulk purchasing agreements to reduce costs and improve supplier relationships.
Outcome: Amazon’s optimized value chain enables it to offer an extensive product selection at competitive prices, driving customer loyalty.
3. Food and Beverage: Fast Food
Company: McDonald’s
- Primary Activities:
- Inbound Logistics: Strong supplier relationships ensuring consistent quality of ingredients.
- Operations: Standardized food preparation processes that ensure speed and consistency.
- Outbound Logistics: Efficient drive-thru and delivery services.
- Marketing and Sales: Iconic branding and localized promotional campaigns.
- Service: Quick service and effective customer feedback mechanisms.
- Support Activities:
- Firm Infrastructure: Centralized management systems for franchise support and operations.
- Human Resource Management: Comprehensive training programs for employees to ensure quality service.
- Technology Development: Adoption of digital ordering systems to enhance customer convenience.
- Procurement: Strategic partnerships with suppliers for bulk purchasing and quality assurance.
Outcome: McDonald’s leverages its value chain to provide fast, affordable meals while maintaining a strong global brand.
4. Technology: Software Development
Company: Microsoft
- Primary Activities:
- Inbound Logistics: Collaboration with third-party developers and open-source communities.
- Operations: Agile development processes for rapid software updates.
- Outbound Logistics: Digital distribution through platforms like Microsoft Store and cloud services.
- Marketing and Sales: Targeted B2B marketing strategies for enterprise solutions.
- Service: Comprehensive customer support and extensive online resources.
- Support Activities:
- Firm Infrastructure: Strong management practices ensuring alignment across business units.
- Human Resource Management: Continuous learning and development programs for employees.
- Technology Development: Investment in R&D for innovative software solutions.
- Procurement: Strategic sourcing of software tools and platforms to enhance development capabilities.
Outcome: Microsoft’s efficient value chain allows it to deliver innovative software solutions swiftly, maintaining high customer satisfaction.
5. Healthcare: Pharmaceuticals
Company: Pfizer
- Primary Activities:
- Inbound Logistics: Sourcing high-quality raw materials from multiple suppliers.
- Operations: Advanced R&D processes for drug formulation and testing.
- Outbound Logistics: Efficient distribution networks for timely medication delivery.
- Marketing and Sales: Targeted campaigns aimed at healthcare professionals and consumers.
- Service: Patient support programs for medication management.
- Support Activities:
- Firm Infrastructure: Strong governance and compliance systems to meet regulatory standards.
- Human Resource Management: Recruitment of top scientists and ongoing training in compliance and ethics.
- Technology Development: Investment in innovative research technologies and data analytics.
- Procurement: Strategic sourcing to ensure reliable supply chains for critical materials.
Outcome: Pfizer’s comprehensive value chain enables it to develop and deliver new medications effectively, maintaining a leading position in the industry.
The Power of Visualizing Value Chain Analysis
Visualizing Value Chain Analysis through infographics enhances understanding and communication of complex information. Here’s why using infographics can be particularly beneficial:
Benefits of Visualizing Value Chain Analysis
- Clarity and Simplicity: Infographics distill complex processes into easily digestible visuals. This helps stakeholders quickly grasp how each activity contributes to overall value.
- Increased Engagement: Visual content is more engaging than text-heavy reports. Infographics can capture attention and maintain interest, making it easier to convey important insights.
- Enhanced Communication: Infographics facilitate better communication among team members and across departments. They provide a common reference point that can lead to more productive discussions.
- Quick Reference: A well-designed infographic serves as a quick reference guide. Stakeholders can easily revisit the visual to recall key components of the value chain without wading through lengthy documents.
- Better Memory Retention: Visual aids enhance memory retention. People are more likely to remember information presented visually, which can lead to better decision-making and strategic planning.
- Highlighting Relationships: Infographics can effectively illustrate the relationships and interdependencies between various activities within the value chain, showcasing how improvements in one area can impact others.
Tools for Creating Infographics
If you’re looking for an easy-to-use tool to create compelling infographics for Value Chain Analysis, Visual Paradigm Online is an excellent choice. Here’s why:
- User-Friendly Interface: Visual Paradigm Online provides a straightforward drag-and-drop interface, making it accessible for users with varying design skills.
- Customizable Templates: The platform offers a wide range of customizable infographic templates specifically designed for business analysis, including value chains.
- Collaboration Features: Visual Paradigm Online allows for real-time collaboration, enabling team members to work together seamlessly, regardless of location.
- Integration Capabilities: The tool can integrate with other applications, making it easier to incorporate data and insights into your infographics.
- Export Options: You can easily export your infographics in various formats for presentations, reports, or online sharing.
Conclusion
Value Chain Analysis is an essential tool for any organization aiming to improve its operations and enhance its competitive edge. By systematically evaluating activities and their contributions to value creation, businesses can make informed decisions that lead to better performance and customer satisfaction. Whether as part of a major strategic initiative or an ongoing improvement program, VCA provides the insights necessary for success in today’s dynamic business environment.
These examples demonstrate how Value Chain Analysis, encompassing both primary and support activities, helps businesses identify areas for improvement. By optimizing the entire value chain, organizations can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver greater value to customers, ultimately strengthening their competitive advantage.
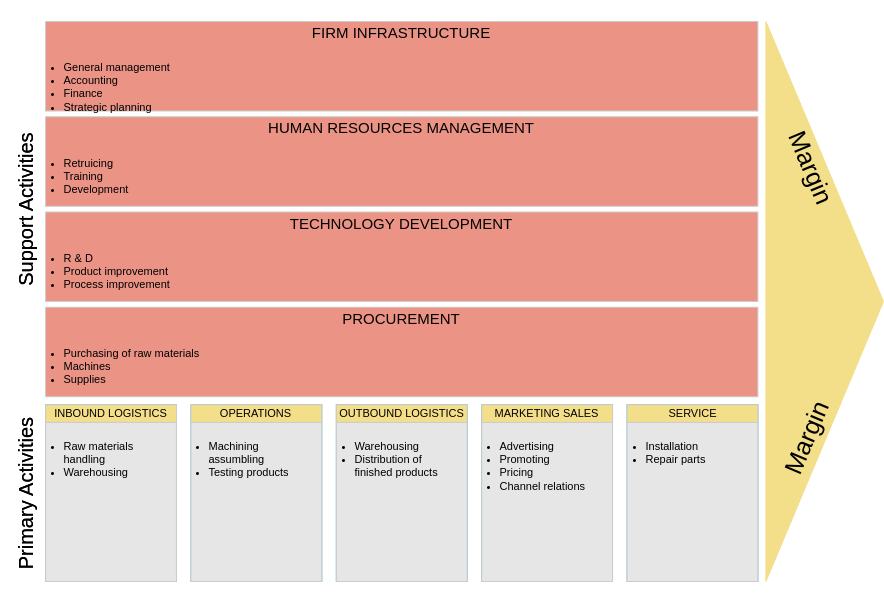
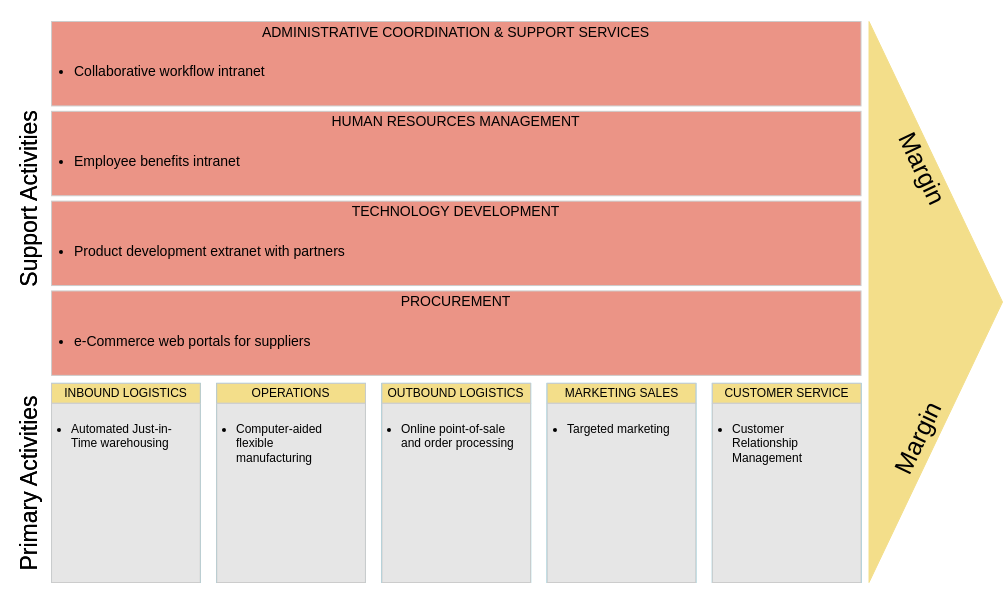
Value Chain Analysis Templates