What is SOAR Analysis?
SOAR analysis is a strategic planning tool that focuses on an organization’s Strengths, Opportunities, Aspirations, and Results. Unlike traditional SWOT analysis, which also considers weaknesses and threats, SOAR emphasizes a positive, forward-looking approach. It encourages teams to build on existing strengths and opportunities while envisioning future aspirations and defining measurable results.
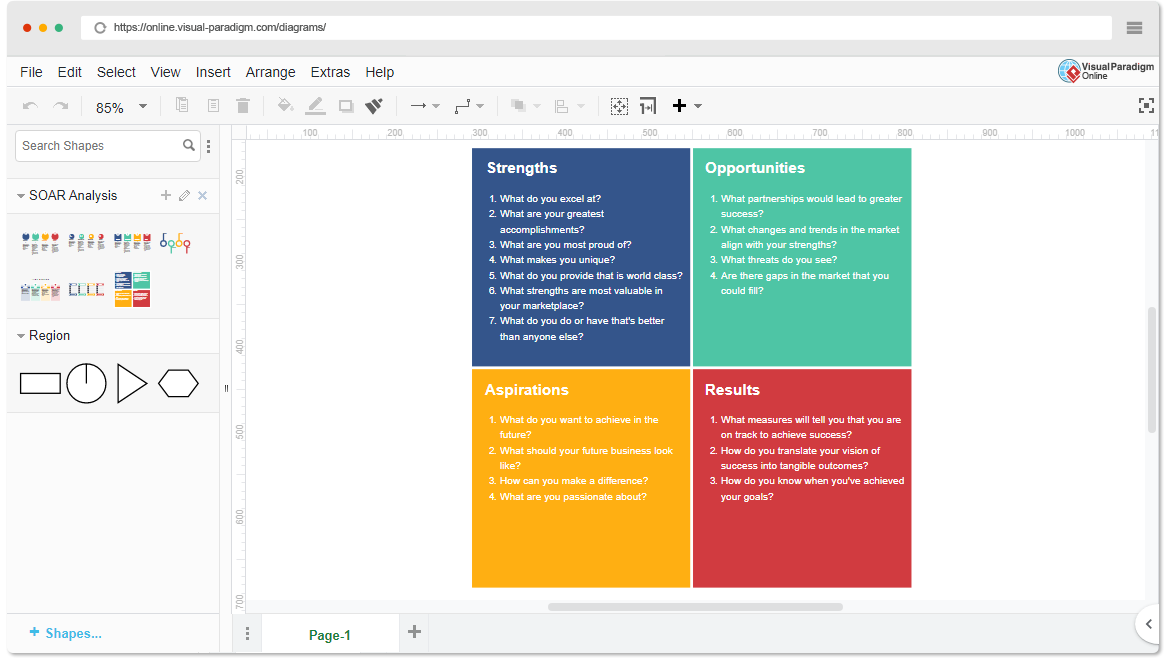
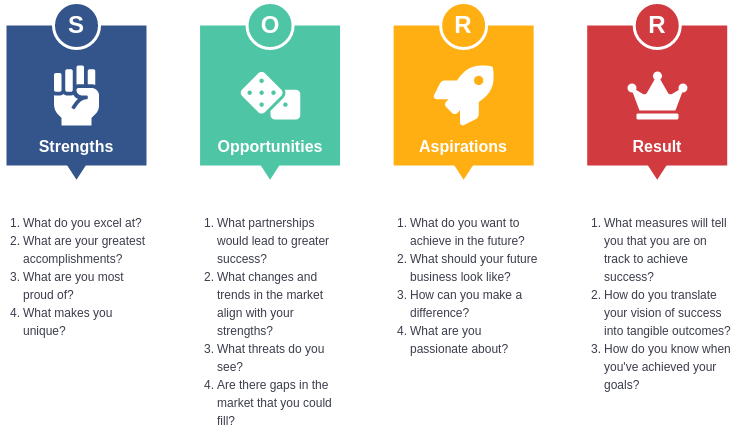
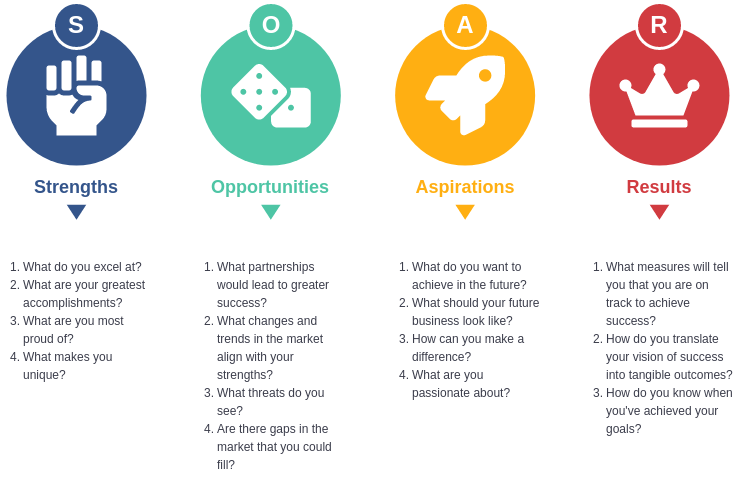
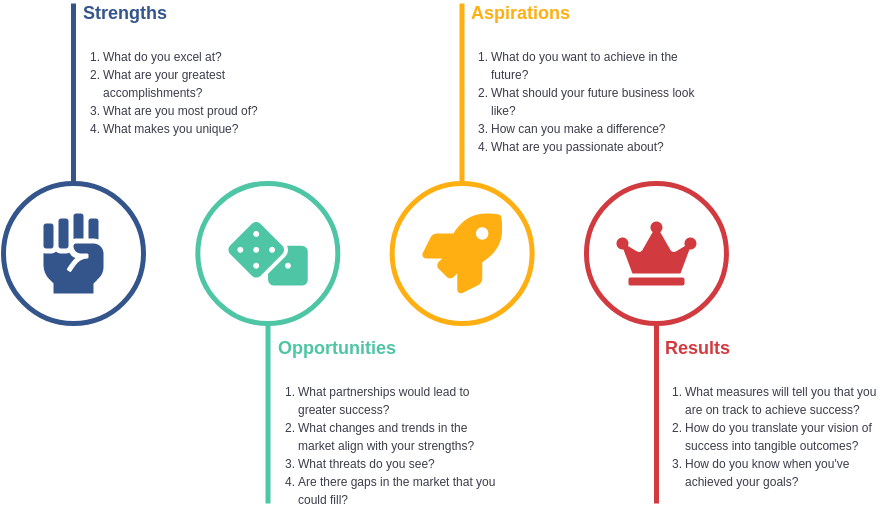
Components of SOAR:
- Strengths: Identify what your organization does well. This includes resources, capabilities, and unique advantages.
- Opportunities: Explore external factors that your organization can leverage, including market trends, technological advancements, and potential partnerships.
- Aspirations: Define the vision and desired outcomes for the future. This involves setting ambitious, yet achievable goals that align with the organization’s mission.
- Results: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress towards achieving aspirations. This ensures accountability and helps track success.
Why Use SOAR Analysis?
SOAR analysis is beneficial for several reasons:
- Positive Focus: By concentrating on strengths and opportunities, SOAR fosters a constructive mindset, which can enhance team morale and motivation.
- Alignment: It aligns teams around a shared vision and common goals, promoting collaboration and unity.
- Strategic Clarity: By defining clear aspirations and measurable results, organizations can create a focused strategic plan that directs efforts effectively.
- Adaptability: SOAR is flexible and can be adapted to various contexts, from startups to large enterprises, making it a versatile tool for strategic planning.
Who Should Use SOAR Analysis?
SOAR analysis can be applied by:
- Leadership Teams: To set the strategic direction and vision for the organization.
- Project Managers: To align project goals with organizational strengths and opportunities.
- Marketing Teams: To identify market opportunities and define clear objectives for campaigns.
- Nonprofits and Community Organizations: To clarify goals and enhance community impact.
When to Use SOAR Analysis?
SOAR analysis is particularly useful in the following scenarios:
- Strategic Planning: When developing or revising strategic plans to align with a changing environment.
- Project Initiation: At the start of new initiatives or projects to ensure alignment with organizational goals.
- Performance Reviews: During assessments of organizational performance and when setting future objectives.
- Crisis Management: To pivot and refocus efforts after a setback, emphasizing strengths and opportunities for recovery.
How to Conduct a SOAR Analysis
Conducting a SOAR analysis involves several steps:
- Gather a Diverse Team: Include members from different departments to ensure a variety of perspectives.
- Facilitate a Workshop: Organize a session where team members can collaboratively discuss each component of SOAR.
- Identify Strengths: Brainstorm and list the organization’s key strengths. Consider internal capabilities, resources, and unique selling propositions.
- Explore Opportunities: Analyze external factors that could benefit the organization. This could involve market research, competitor analysis, or trend identification.
- Define Aspirations: Encourage participants to articulate their vision for the organization. What do they want to achieve in the next 3-5 years?
- Set Measurable Results: Determine KPIs that will help track progress towards the defined aspirations. Ensure these are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Document and Communicate: Compile the findings into a clear and concise document. Share it with the organization to create awareness and buy-in.
- Review and Adjust: Regularly revisit the SOAR analysis to assess progress and make adjustments as necessary.
Case Study: SOAR Analysis at GreenTech Innovations
Background
GreenTech Innovations is a mid-sized company specializing in sustainable energy solutions. Founded in 2015, the organization has rapidly expanded its market presence by offering innovative solar panel technologies and energy-efficient systems. However, amidst rising competition and changing market dynamics, the leadership team recognized the need for a strategic review to guide future growth.
Objective
The primary objective of this SOAR analysis was to align the company’s resources and aspirations with market opportunities while fostering a positive organizational culture.
SOAR Analysis Process
Step 1: Forming the Team
The leadership team assembled a diverse group of employees from various departments, including R&D, marketing, sales, and customer service. This ensured a broad perspective on the company’s strengths and opportunities.
Step 2: Conducting the Workshop
A two-day workshop was organized to facilitate discussions among team members. The session was structured around the four components of SOAR.
Step 3: Identifying Strengths
During the workshop, participants identified several key strengths:
- Innovative Products: GreenTech is known for its cutting-edge solar technology, which offers higher efficiency than competitors.
- Skilled Workforce: The company boasts a team of highly qualified engineers and technicians.
- Strong Brand Reputation: GreenTech has established itself as a leader in sustainable practices, which resonates with environmentally conscious consumers.
Step 4: Exploring Opportunities
The team then explored external opportunities:
- Growing Demand for Renewable Energy: With increasing awareness of climate change, there is a rising demand for sustainable energy solutions.
- Government Incentives: Various government programs encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies, providing financial incentives for consumers and businesses.
- Partnership Opportunities: Collaborations with other tech firms and research institutions could enhance product development.
Step 5: Defining Aspirations
Participants articulated the company’s long-term aspirations:
- Market Leadership: To become the leading provider of sustainable energy solutions in North America within five years.
- Product Diversification: To expand the product line to include energy storage solutions and smart home technologies.
- Global Expansion: To enter international markets, particularly in Europe and Asia, where renewable energy demand is high.
Step 6: Setting Measurable Results
The team established clear KPIs to measure progress toward their aspirations:
- Market Share Growth: Increase market share by 15% annually over the next five years.
- Product Launches: Introduce at least three new products each year.
- Customer Satisfaction: Achieve a customer satisfaction score of 90% or higher based on feedback and surveys.
Step 7: Documenting and Communicating Findings
The findings from the SOAR analysis were documented in a comprehensive report. This report included the identified strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and measurable results. It was shared with all employees during a company-wide meeting to ensure transparency and foster a collective commitment to the strategic plan.
Step 8: Review and Adjust
The leadership team scheduled quarterly reviews to assess progress against the established KPIs and adjust strategies as needed. This ongoing evaluation ensured that the company remained agile and responsive to market changes.
Results
Within two years of implementing the SOAR analysis findings, GreenTech Innovations achieved significant milestones:
- Market Share Increase: The company successfully grew its market share by 20%, surpassing its initial goal.
- New Products: GreenTech launched five new products, including a highly successful energy storage system that complemented its solar offerings.
- Customer Satisfaction: The customer satisfaction score improved to 92%, reflecting the company’s commitment to quality and service.
SWOT vs. SOAR Analysis: A Comparative Overview
Both SWOT and SOAR analyses are strategic planning tools used by organizations to evaluate their position and develop strategies for the future. However, they differ significantly in focus, approach, and application. Here’s a detailed comparison.
1. Definition
SWOT Analysis
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It is a framework that helps organizations identify internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats.
SOAR Analysis
SOAR stands for Strengths, Opportunities, Aspirations, and Results. This tool emphasizes a positive, future-oriented approach, focusing on leveraging strengths and opportunities to achieve aspirations and measurable results.
2. Focus
SWOT Analysis
- Internal and External: SWOT analyzes both internal factors (strengths and weaknesses) and external factors (opportunities and threats).
- Balanced View: It provides a balanced view of the organization, including challenges and limitations.
SOAR Analysis
- Positive Orientation: SOAR focuses primarily on strengths and opportunities, promoting a constructive mindset.
- Vision-Driven: It emphasizes aspirations and results, aligning strategies with the organization’s vision for the future.
3. Structure
SWOT Analysis
- Four Quadrants: SWOT is typically presented in a four-quadrant matrix, making it easy to visualize the relationships between different factors.
- Descriptive: Each quadrant contains a list of factors that describe the organization’s current situation.
SOAR Analysis
- Four Components: SOAR is structured around Strengths, Opportunities, Aspirations, and Results but does not use a matrix format.
- Goal-Oriented: It encourages organizations to define clear aspirations and measurable results, guiding strategic direction.
4. Application
SWOT Analysis
- Versatile Use: SWOT can be applied in various contexts, including project planning, competitive analysis, and organizational assessments.
- Problem Identification: It is often used to identify problems and challenges, making it useful in crisis management.
SOAR Analysis
- Strategic Planning: SOAR is typically used in strategic planning sessions to align teams around a shared vision and objectives.
- Team Collaboration: It encourages collaboration and engagement among team members, fostering a collective commitment to achieving goals.
5. Outcomes
SWOT Analysis
- Balanced Insights: Provides a comprehensive view of the organization, helping leaders make informed decisions.
- Actionable Strategies: Identifies potential strategies based on the analysis of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
SOAR Analysis
- Positive Framework: Cultivates a positive organizational culture by focusing on what the organization does well.
- Measurable Goals: Establishes clear aspirations and results, ensuring accountability and tracking progress.
6. When to Use
SWOT Analysis
- Initial Assessments: Best used during initial assessments of an organization or project.
- Crisis Situations: Helpful when addressing urgent issues or challenges.
SOAR Analysis
- Vision Development: Ideal for developing or refining an organization’s long-term vision.
- Strategic Alignment: Useful when aligning teams around common goals and objectives.
Here’s a summary table comparing SWOT and SOAR analyses:
| Feature | SWOT Analysis | SOAR Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats | Strengths, Opportunities, Aspirations, Results |
| Focus | Internal and external factors | Positive orientation and future aspirations |
| Structure | Four-quadrant matrix | Four-quadrant matrix |
| Application | Versatile use in various contexts | Primarily used for strategic planning |
| Outcomes | Balanced insights and actionable strategies | Positive framework with measurable goals |
| When to Use | Initial assessments and crisis situations | Vision development and strategic alignment |
| Team Engagement | Varies; can be individual or team-based | Encourages team collaboration and engagement |
This table provides a clear comparison of the two analyses, highlighting their key features and applications.
Conclusion
SOAR analysis is a powerful tool for organizations looking to harness their strengths and seize opportunities. By focusing on aspirations and results, it not only helps in strategic planning but also fosters a positive organizational culture. Whether you are a leader, project manager, or part of a marketing team, incorporating SOAR into your planning process can pave the way for sustainable growth and success.
The SOAR analysis facilitated a transformative strategic direction for GreenTech Innovations. By focusing on strengths and opportunities, the company not only solidified its market position but also fostered a culture of collaboration and innovation. This case study exemplifies how SOAR analysis can effectively guide organizations toward sustainable growth and success.
Both SWOT and SOAR analyses are valuable tools for strategic planning, but they serve different purposes and approaches.
- SWOT provides a balanced overview, including challenges and limitations, making it suitable for comprehensive assessments.
- SOAR focuses on strengths and opportunities, promoting a positive outlook and a clear path to achieving aspirations.
Organizations may choose to use either or both methods, depending on their specific needs and the context of their strategic planning efforts.
Visual Paradigm Online – SOAR Analysis Templates